Full-Stack 개발자가 되려는 작은 개발자의 블로그
객체지향 실습5 본문
Collection
- 여러 객체(데이터)를 모아 놓은 프레임워크
- 데이터는 리터럴(실제 값, 숫자, 문자)과 인스턴스(문자열, 배열, 개발자가 정의한 클래스로 만든 인스턴스)를 모아 저장
- 배열의 단점인 크기가 정해진다는 부분을 해결하여 동적으로 데이터를 저장하기 위해 만들어졌다.
| Set | 집합. 순서 없고, 중복된 데이터를 저장 할 수 없음 |
| List | 목록. 순서를 가지며, 중복된 데이터를 저장 가능 |
| Map |
키와 값의 쌍으로 데이터를 저장. 키는 중복 될 수 없으며, 값은 중복 될 수 있음. 순서를 가지지 않음 |
Iterator
- Collection 클래스들을 순자 구조로 변환하여 사용하기 위한 구조 클래스
- Set의 경우 비순차적으로 데이터를 저장하기 때문에 Iterator로 변환하여 데이터를 사용.
| boolean hasNext() | 처리 할 다음 요소가 있는지 확인하는 메소드 |
| Object next() | 다음 순번의 요소를 가지고 오는 메소드 |
| void remove() | 가지고 온 요소를 삭제하는 메소드 |
※ ArrayList에서 Iterator를 사용하는 경우 요소의 삭제(remove)를 안전하게 처리 할 경우 사용.
< Set >
Set<Integer> iSet = new HashSet<>();
iSet.add(1);
iSet.add(2);
iSet.add(9);
iSet.add(11);
iSet.add(5);
iSet.add(3);
iSet.add(10);
System.out.println(iSet);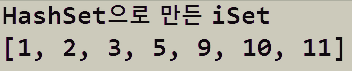
Iterator<Integer> iter = iSet.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
int i = iter.next();
System.out.println(i);
}
< List >
List<Integer> iList = new ArrayList<>();
iList.add(1);
iList.add(2);
iList.add(2);
iList.add(2);
iList.add(2);
iList.add(2);
iList.add(2);
iList.add(5);
System.out.println("ArrayList로 만든 iList");
System.out.println(iList);
ArrayList를 삭제 시 발생하는 문제
//forEach로 삭제
for(Integer k : iList) {
if(k == 2) {
iList.remove(2);
}
}
//for로 삭제
//iList값이 초기 정해져 있어 삭제 진행 이후 iList의 범위를 초과하여 반복
int size=iList.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int k = iList.get(i);
if(iList.get(i) == 2) {
iList.remove(i);
size--;
i--;
}
}※ 반복문이 실행 도중 객체의 구조적 변경(객체배열의 사이즈 변경과 같은)이 일어나 ConcurrentModificationException이 발생한다.
Iterator를 이용한 안전한 요소 삭제
Iterator<Integer> iterlist = iList.iterator();
while(iterlist.hasNext()) {
if(iterlist.next() == 2) {
iterlist.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(iList);
Map 인터페이스
- HashMap<K, V>
▶ 키(key)와 값(value)의 쌍으로 구성되는 요소를 저장하고 처리하는 컬렉션
▶ 값을 검색하기 위해 키를 사용
▶ 키에 해당하는 자료형(data type)은 주로 문자열을 사용.
▶ 값에는 모든 기본 자료형, 인스턴스가 들어갈 수 있다.
| put() | 요소를 추가하기 위한 메소드 |
| get(key) | 키에 해당하는 요소를 불러오는 메소드 |
package map;
import java.util.*;
public class HashMapTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> dictionary = new HashMap<String, String>();
dictionary.put("apple", "사과");
dictionary.put("Ship", "배");
dictionary.put("Grape", "포도");
dictionary.put("Ship", "돗단배");
dictionary.put("Snow", "눈");
dictionary.put("Eye", "눈");
String kor = dictionary.get("apple");
System.out.println("apple의 한글은 "+ kor);
kor = dictionary.get("Ship");
System.out.println("Ship의 한글은 "+ kor);
kor = dictionary.get("Snow");
System.out.println("Snow의 한글은 "+ kor);
kor = dictionary.get("Eye");
System.out.println("Eye의 한글은 "+ kor);
//키 목록을 구할 때 사용하는 메소드 : keySet();
Set<String> keyList = dictionary.keySet();
System.out.println(keyList);
//값 목록을 구할 때 사용하는 메소드 : values();
Collection<String> valueList = dictionary.values();
System.out.println(valueList);
//찾고자 하는 키가 있는지 : containsKey();
System.out.println("apple이 있나요? " + dictionary.containsKey("apple"));
//찾고자 하는 값이 있는지 : containsValue();
System.out.println("배가 있나요? " + dictionary.containsValue("돗단배"));
//키로 값을 삭제(키도 같이 삭제 됨)
dictionary.remove("Ship");
System.out.println(dictionary);
//맵의 크기 구하기 : size()
int mapsize = dictionary.size();
System.out.println(mapsize);
//전체 삭제 : clear();
dictionary.clear();
//value 부분에 정수를 저장하는 Map
Map<String, Integer> menu = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
//입력 예
menu.put("apple", 500);
}
}

'강의 정리 > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| JAVA_JDBC연동 (0) | 2020.05.04 |
|---|---|
| 학교 인적 관리 프로그램(SchoolPrj) (0) | 2020.04.18 |
| 객체 지향 실습 4 (0) | 2020.04.07 |
| 객체 지향 실습2 (0) | 2020.04.01 |
| 물품 관리 프로그램(Homeminus) (1) | 2020.04.01 |
Comments


